4mm galvanized sheet, 3mm, 4.75mm, 5mm galvanized sheets, processing of galvanized sheets
Category:
Summary description:
Keywords:
Details
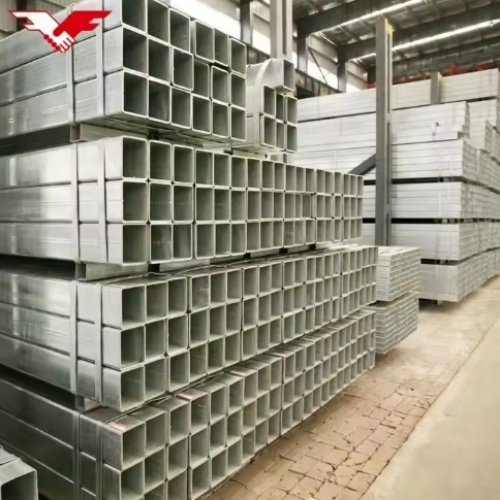
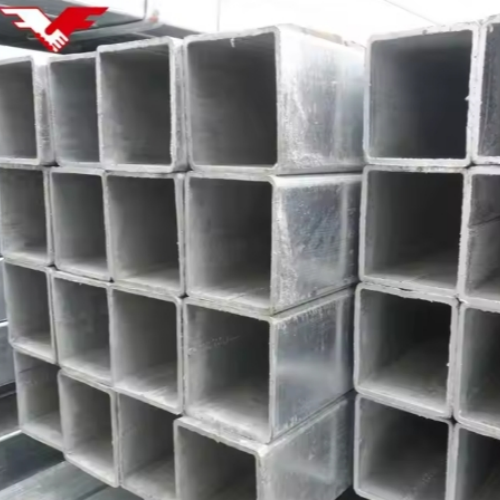
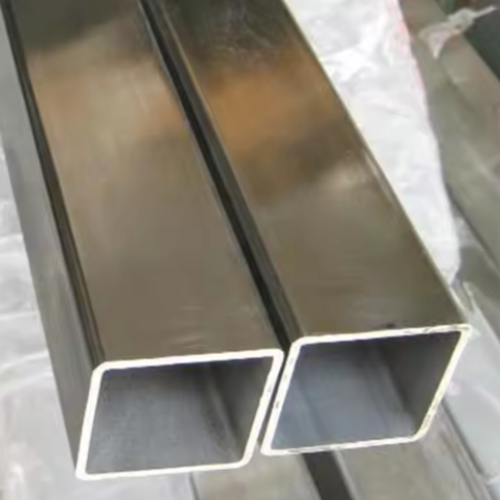
Galvanized sheets are widely used in various industries due to their excellent anti-corrosion properties and durability. In this article, we will focus on several common specifications of galvanized sheets, namely 4mm, 3mm, 4.75mm, and 5mm, as well as the processing of galvanized sheets.
The 4mm galvanized sheet strikes a balance between strength and flexibility. With a moderate thickness, it is suitable for a wide range of applications. In the construction industry, it can be used for the fabrication of structural components such as roof trusses and support frames. Its galvanized coating provides a robust barrier against rust and corrosion, ensuring the long - term stability and safety of the structures. For example, in large - scale industrial buildings, the 4mm galvanized sheet can withstand heavy loads and adverse weather conditions, maintaining its integrity over time.
The 3mm galvanized sheet, on the other hand, is relatively thinner. This characteristic makes it more malleable and easier to work with in certain manufacturing processes. It is often employed in the production of household appliances. For instance, the outer casings of refrigerators and washing machines are frequently made from 3mm galvanized sheets. The thinness allows for more complex shaping and bending operations during the manufacturing stage, while the galvanized layer still offers reliable protection against environmental factors that could cause the metal to deteriorate.
The 4.75mm galvanized sheet occupies a position between the 4mm and 5mm sheets in terms of thickness. This specification is often preferred in scenarios where a slightly enhanced strength compared to the 4mm sheet is required, but the weight and cost implications of using a 5mm sheet need to be avoided. In the automotive industry, it can be used for the production of parts that need to endure mechanical stress, such as certain brackets and mounts. The galvanized surface not only protects the metal from rust but also reduces the need for frequent maintenance, which is crucial for the automotive sector where cost - effectiveness and long - term performance are highly valued.
The 5mm galvanized sheet is one of the thicker options among these commonly used specifications. It offers superior strength and load - bearing capacity. This makes it an ideal choice for heavy - duty applications. In bridge construction, for example, 5mm galvanized sheets can be used in the fabrication of critical structural elements. The high - strength nature of the 5mm sheet enables it to support the significant weight of the bridge and the traffic it carries, while the galvanized coating safeguards it from the corrosive effects of moisture, salt, and other environmental pollutants present in many bridge - building environments.
When it comes to the processing of galvanized sheets, there are several key techniques. One of the most common is cutting. Depending on the required size and shape of the final product, different cutting methods can be employed. Mechanical cutting, such as using shears or circular saws, is suitable for straight cuts and can handle various thicknesses of galvanized sheets. For more complex and precise cutting requirements, laser cutting has become increasingly popular. Laser cutting can create intricate shapes with high accuracy, making it suitable for the production of parts with specific design requirements.
Bending is another important processing method. Bending galvanized sheets allows for the creation of three - dimensional components. Press brakes are commonly used for this purpose. The operator can control the angle and radius of the bend to achieve the desired shape. This process is essential in the production of products like ventilation ducts, which require bent galvanized sheets to form the proper channels for air flow.
Welding is also a significant aspect of galvanized sheet processing. However, when welding galvanized sheets, special precautions need to be taken. The zinc coating on the sheet can vaporize during the welding process, producing harmful fumes. Therefore, proper ventilation and safety equipment are necessary. Different welding techniques, such as arc welding and spot welding, can be used depending on the application. Arc welding is suitable for joining larger sections of galvanized sheets, while spot welding is often used for thinner sheets and in applications where a series of discrete welds are required.
In addition to these basic processing methods, surface finishing of galvanized sheets may also be carried out. This can include painting, powder coating, or applying protective films. These surface finishing processes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the galvanized sheet products but also further improve their corrosion resistance and durability, allowing them to meet the diverse requirements of different industries and applications. Overall, understanding the characteristics of different - sized galvanized sheets and the various processing techniques is essential for maximizing their potential in a wide range of manufacturing and construction projects.
More Products
Message
All Rights Reserved Copyright © RIZHAO STEEL HOLDING GROUP CO.,LTD. SEO 【Business license】
All Rights Reserved Copyright © RIZHAO STEEL HOLDING GROUP CO.,LTD.